


The most important styrene monomer is a colorless liquid like other aromatic substances of Babu.
Its boiling point is 146 degrees Celsius and its density is 0.9 grams per cubic centimeter.
Other names: Styron, Bapolan PS, Edistir, Hostyren
Solvents: Diethyl ether, Toluene, Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
Styrene is mostly used in the processing of polystyrene plastics.
The major method of styrene processing is through ethyl benzene. First, benzene is alkylated with ethylene.
It is then dehydrogenated on an aluminum chloride catalyst, solid phosphoric acid or silica-alumina to styrene.
Polystyrene was first produced in 1940 by the German company I.G.Farben Industries and used as insulation in the electrical industry.
During World War II, when natural rubber entered the United States, the polymer was used as synthetic rubber in the United States.
After the war, when natural rubber began to enter the United States, the consumption of styrene was much lower than its production.
Hence, extensive marketing began for the use of polystyrene in everyday use, until the introduction of its superior properties compared to other polymers, which included high transparency and ductility and low price, today polystyrene is one of the most famous plastics in the industry. is used.
This product was produced for the first time in Iran in 1334 by the efforts of Ionolite Company; Hence in Iran it is known as Ionolite.
The combination of ethylene and benzene produces ethyl benzene, and by hydrogenation from ethyl benzene, styrene is obtained.
Styrene is polymerized with the help of oxygen, oxidizing agent or light as a catalyst during the free radical polymerization process and polystyrene is produced. Polystyrene is a polymer of the vinyl family
Structurally, it has a long hydrocarbon chain that is attached to each carbon atom by a phenyl group.
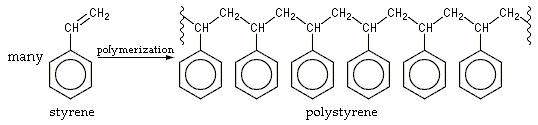
Physical properties
The specific gravity of polystyrene is about 1.09 – 1.04 and it softens at 90 degrees Celsius.
This polymer is hard, brittle and transparent and transmits ordinary light up to about 90%.
Moisture absorption by this polymer is very low and is about 0.03 to 0.1% by weight.
The polymer is also an excellent insulator in terms of electricity.
Polystyrene is soluble in most solvents such as aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene and toluene), chlorine hydrocarbons (tetrachlorocarbon, chloroform, trichlorethylene and dichlorobenzene), methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate and acetaminophen.
Ordinary, dilute acids and alkalis are ineffective on polystyrene.
Oxygen with ozone in the presence of light and especially in heat affect polystyrene.
One of the easiest ways to identify polystyrene is by its flammability:
Polystyrenes burn in the flame and continue to burn after the flame is removed.
It has a yellow flame.
Black smoke with carbon particles.
It drips in the flame.
It smells like burning natural gas.
The most important suspension polymerization of polystyrene:
In suspension polymerization, a catalyst dissolves in the monomer and then disperses in water.
A separate suspending agent is added to stabilize the resulting suspension.
Polymer particles are 0.1 mm to 1 in size.
The polymerization rate and other characteristics are similar to those in mass polymerization.
Common suspending agents include polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylic acid, gelatin, cellulose and pectins.
Inorganic suspending agents include phosphates, aluminum hydroxide, zinc oxide, magnesium silicate and kaolin.
Suspension polymerization, which leads to the control of the size and size distribution of polymer particles, is more an art than a science.
The design of the reactor and the stirrer play an important role in the shear distribution inside the reactor, which can have a great effect on the particle size.
Other factors that affect the size of polymers and their distribution are the ratio of monomer to water or solvents, the reaction temperature, the type of primers and their consumption, and the suspending agent.
Preparation of a polymer with coarser polystyrene particles, which is a single distribution, by a special fan, which is the suspension polymerization of the grain.
In addition, the effect of using ultrasound to suspend styrene polymerization has been proven.
Mass polymerization involves heating the solvent-free monomer with the initiator, usually benzoyl peroxide
In a container.
The monomer-primer mixture will be polymerized as a solid, in the form of a container.
One of the most important practical disadvantages of this method is the separation of the polymer from the reactor or balloon and the diffusion and extraction of heat generated
By polymerization.
This method is used to produce parts by casting or molding, such as igniters
Plastic is used in small or large shapes, but this
The work is problematic because hot spots or defects on the part must be avoided.
When polystyrene is used, the polymerization reaction generates 17 Kcal / mol (polymerization heat) of heat.
The polystyrene that is produced has a wide molecular weight distribution and poor mechanical properties.
The residual monomer in the polymer can be removed using effective escape devices.
Polymerization was introduced as a mass of polystyrene with a narrow molecular weight distribution in a US patented invention.
Several distributions reported 2.6 with a conversion of 93%, and stated that the numerical average molecular weight was about 100,000. This was achieved by polymerizing styrene in the presence of 1%, 4-tert-butyl pyrcactol at 127 ° C for 2.27 hours.
Heating without the presence of the mentioned substance will lead to the production of a polymer with several distributions of 3.3 and a numerical average molecular weight of 79,200. Controlled evaporation of inactive monomers is one way to remove the reaction heat.
Operation on polystyrenes is usually done by injection method, but due to the excellent processability of this material, other methods also work well.
Different types of polystyrene are resistant to a wide range of chemicals (bases, salts, alcohols and weak acids).
Polystyrenes also comply with FDA regulations (for use in the food industry).
This polymer is made in two stages, first at 80 ° C and then at room temperature
They produce between 100 and 180 degrees Celsius.
Today, polystyrene accounts for about 12% of the market for soft heat plastics.
Polystyrene is softened at 90 ° C and melted and molded at 190 to 250 ° C.
Production of General purpose polystyrene with different grades

info@artanpetro.com
Qom Shokouhieh Industrial Town, end of the second phase, Babaei Square, Babaei St., Alam al-Huda St. 1, No. 1331
+982533346396![]()
+982533346473![]()